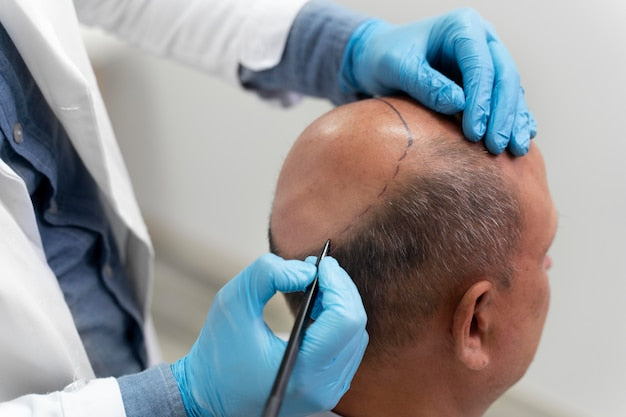
Hair Transplant Method
There are two main methods of hair transplantation: Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) and Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT). These methods differ in how the donor hair follicles are harvested and transplanted.
-
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE): FUE is a minimally invasive technique that involves the extraction of individual hair follicles from the donor area, typically the back or sides of the scalp. The surgeon uses a small, circular punch tool to remove the follicles one by one. This method does not require the removal of a strip of tissue, which is a key difference from FUT. Once extracted, the hair follicles are transplanted into the recipient area (bald or thinning areas) of the scalp. FUE leaves small, dot-like scars that are less noticeable than the linear scar associated with FUT. FUE also allows for greater flexibility in harvesting hair from various parts of the body, if needed.
-
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT): FUT involves the surgical removal of a thin strip of tissue from the donor area, usually the back of the scalp. This strip is then dissected under a microscope into individual hair follicles, which are subsequently transplanted into the recipient area. FUT allows for the transplantation of a large number of grafts in a single session, making it suitable for individuals who require significant hair restoration. However, it does leave a linear scar at the donor site, which can be concealed by surrounding hair if grown out.
The choice between FUE and FUT depends on various factors, including the patient's specific needs, the available donor hair, the surgeon's expertise, and individual preferences. It's crucial to consult with a qualified hair transplant specialist who can evaluate your situation and recommend the most appropriate method for your hair restoration goals.





